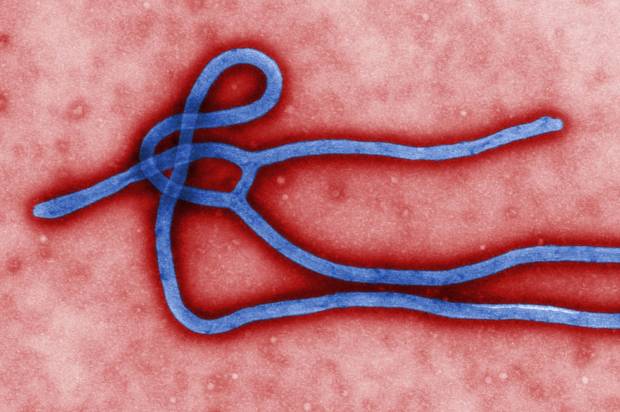
 “The outbreak — the largest in history — has spread across Guinea, Liberia, Nigeria and Sierra Leone and killed at least 672 people, according to the World Health Organization. The disease has no vaccine and no specific treatment. It has a fatality rate of at least 60%.”
“The outbreak — the largest in history — has spread across Guinea, Liberia, Nigeria and Sierra Leone and killed at least 672 people, according to the World Health Organization. The disease has no vaccine and no specific treatment. It has a fatality rate of at least 60%.”
Among the most frightening developments in a world full of bad news at the moment: Ebola is running rampant through West Africa, and has reached both Freetown and Lagos, Africa’s largest city (where it was hopefully and quickly contained.) “This epidemic…can only get worse, because it is still spreading, above all in Liberia and Sierra Leone, in some very important hotspots,’ Janssens said…’we have never known such an epidemic.'”
Still, before you seal the locks on the underground shelter, the general scientific consensus seems to be that, even if the virus does reach here by plane — and it may well — ebola isn’t influenza circa 1918: “This is not a highly transmissible disease, where the number of people who can be infected by a single individual is high. You have to come into very close contact with blood, organs, or bodily fluids of infected animals, including people. If you educate people properly and isolate those who are potentially infected, it should be something you can bring under control.”
Also, as far as deadly mutations go, ebola “kill[s] so quickly that I don’t envision there’s going to be a major shift in transmission.” Some small comfort…unless, of course, you’re infected. As it is, per The Onion, a vaccine is “at least 50 white people“ away.