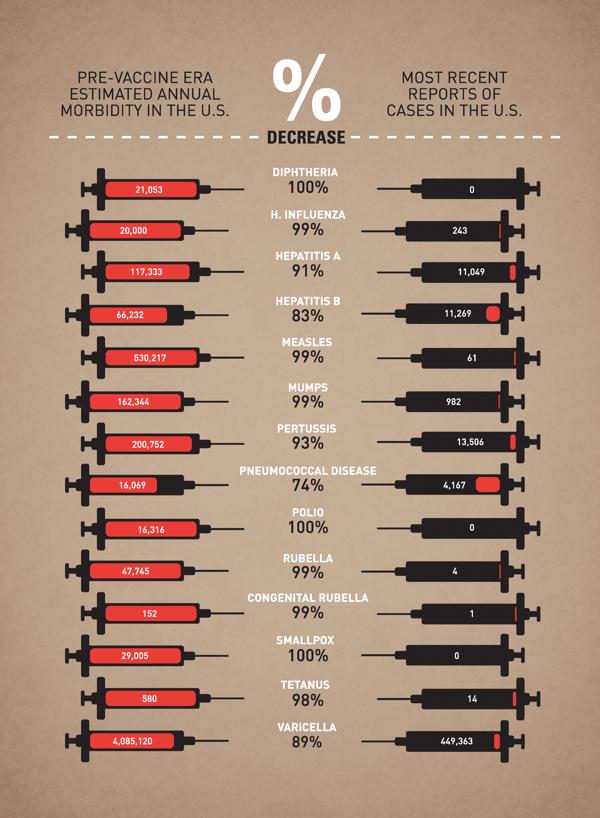
 “The researchers coded each tweet for its happiness content, based on the appearance and frequency of words determined by Mechanical Turk workers to be happy (rainbow, love, beauty, hope, wonderful, wine) or sad (damn, boo, ugly, smoke, hate, lied). While the researchers admit their technique ignores context, they say that for large datasets, simply counting the words and averaging their happiness content produces ‘reliable’ results.”
“The researchers coded each tweet for its happiness content, based on the appearance and frequency of words determined by Mechanical Turk workers to be happy (rainbow, love, beauty, hope, wonderful, wine) or sad (damn, boo, ugly, smoke, hate, lied). While the researchers admit their technique ignores context, they say that for large datasets, simply counting the words and averaging their happiness content produces ‘reliable’ results.”
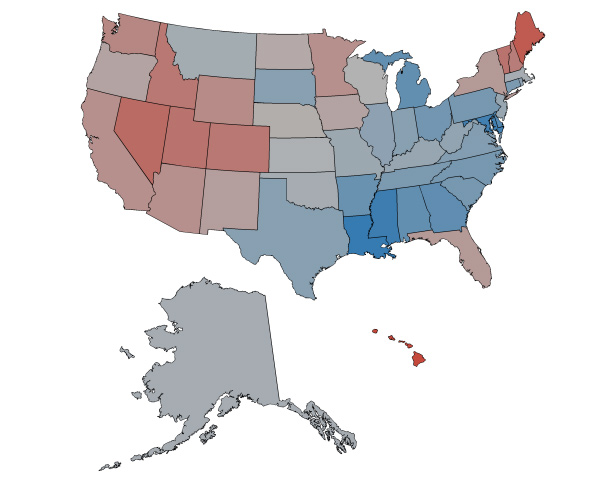
Happiness where are you? I’ve searched so long for you. A statistical analysis of states’ relative happiness, as determined by tweets. (Red states above are happy, blue states are not.) David Simon is 2-for-2: Next to the mouth of the Mississippi, the Maryland-Delaware area is apparently the saddest in the nation. Perhaps due to proximity to Washington DC? Definitely maybe.
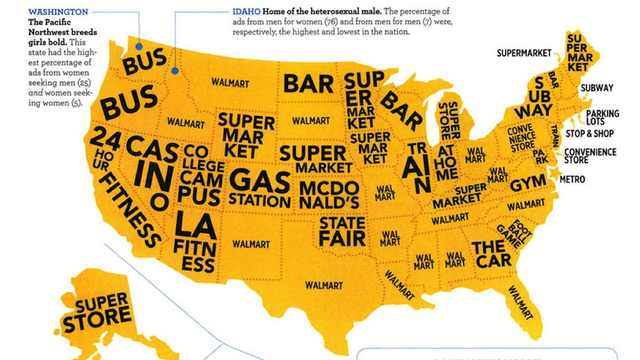
In probably related news, a different map of the United States shows the most popular places cited in Craigslist’s Missed Connections. “The most popular place to spot potential love in Texas, New Mexico, Missouri, Louisiana, Arkansas, Mississippi, Alabama, Idaho, Montana, South Dakota, Ohio, West Virginia, Tennessee, North Carolina and Florida? Wal-Mart.”
Of course, this begs the question: Do people actually ever meet up on Missed Connections? Every time I’ve perused them, that section is overwhelmingly the Boulevard of Broken Dreams, just damaged, lovelorn people sending out messages in a bottle to lost exes who are actively ignoring them.