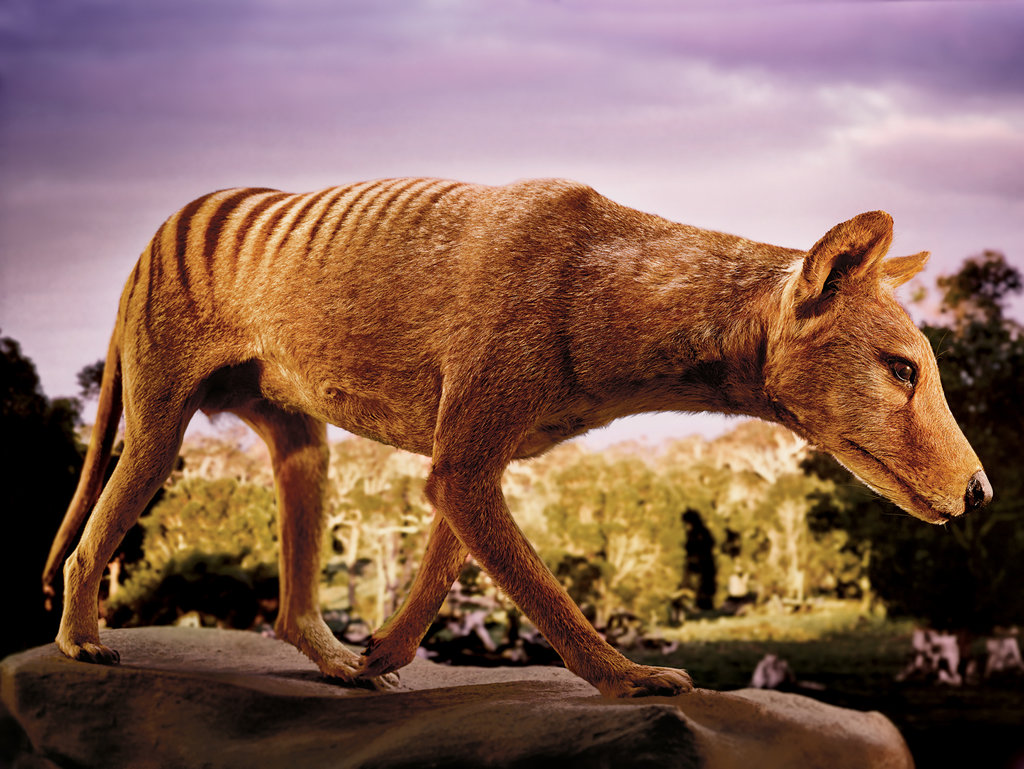
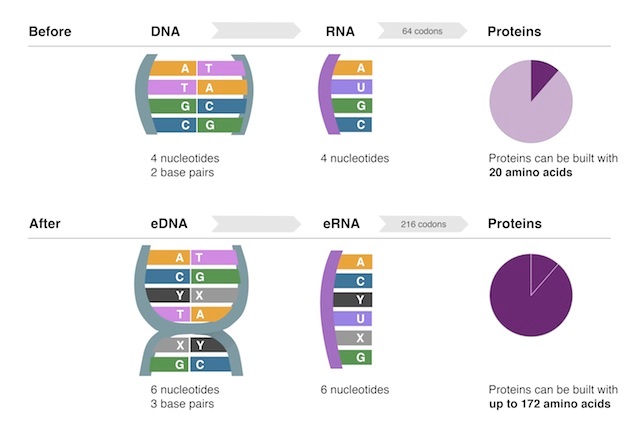
“The earth is about to become a lot less ‘natural.’ Biologists have already created new forms of bacteria in the lab, modified the genetic code of countless living species and cloned dogs, cats, wolves and water buffalo, but the engineering of novel vertebrates — of breathing, flying, defecating pigeons — will represent a milestone for synthetic biology. This is the fact that will overwhelm all arguments against de-extinction.”
“The earth is about to become a lot less ‘natural.’ Biologists have already created new forms of bacteria in the lab, modified the genetic code of countless living species and cloned dogs, cats, wolves and water buffalo, but the engineering of novel vertebrates — of breathing, flying, defecating pigeons — will represent a milestone for synthetic biology. This is the fact that will overwhelm all arguments against de-extinction.”
By way of Follow Me Here, the NYT’s Nathaniel Rich examines the promise, challenges, and ethics of reviving extinct species, and beyond:
“What is coming will go well beyond the resurrection of extinct species. For millenniums, we have customized our environment, our vegetables and our animals, through breeding, fertilization and pollination. Synthetic biology offers far more sophisticated tools. The creation of novel organisms, like new animals, plants and bacteria, will transform human medicine, agriculture, energy production and much else. De-extinction ‘is the most conservative, earliest application of this technology,’ says Danny Hillis, a Long Now board member and a prolific inventor who pioneered the technology that is the basis for most supercomputers.”