 “In a statement issued by the European Space Agency, Jean-Jacques Dordain, its director general, said, ‘The extraordinary quality of Planck’s portrait of the infant universe allows us to peel back its layers to the very foundations, revealing that our blueprint of the cosmos is far from complete.'”
“In a statement issued by the European Space Agency, Jean-Jacques Dordain, its director general, said, ‘The extraordinary quality of Planck’s portrait of the infant universe allows us to peel back its layers to the very foundations, revealing that our blueprint of the cosmos is far from complete.'”
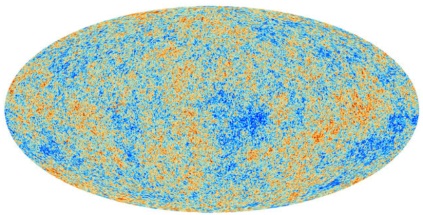
This came out while I was in Seattle and I’ve been meaning to catch up: By measuring the cosmic background radiation still extant from the Big Bang, the ESA’s Planck satellite gives us our most detailed map of the universe yet.
“[T]he new satellite data underscored the existence of puzzling anomalies that may yet lead theorists back to the drawing board. The universe appears to be slightly lumpier, with bigger and more hot and cold spots in the northern half of the sky as seen from Earth than toward the south, for example. And there is a large, unexplained cool spot in the northern hemisphere.”
I find these maps particularly fascinating because, as I said when NASA’s WMAP returned its data in 2003 (and here in 2002), I spent the summer of 1992 poring over the original COBE DMR version of this map for my high school senior thesis, in order to determine whether the radiation exhibited a fractal distribution. (And, honestly, how early 90’s is that?)
“‘A.M.S. has confirmed with exquisite precision and to high energy one of the most exciting mysteries in astrophysics and particle physics,’ said Justin Vandenbroucke, of the University of Wisconsin and Stanford’s SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory.” In related news, NASA’s recently-installed Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer on the ISS is helping physicists and cosmologists get to the bottom of the dark matter mystery.
The A.M.S. has “confirmed previous reports that local interstellar space is crackling with an unexplained abundance of high energy particles, especially positrons, the antimatter version of the familiar electrons that constitute electricity and chemistry…’Over the coming months, A.M.S. will be able to tell us conclusively whether these positrons are a signal for dark matter, or whether they have some other origin.’“








