

Haunting the Web Since 1999


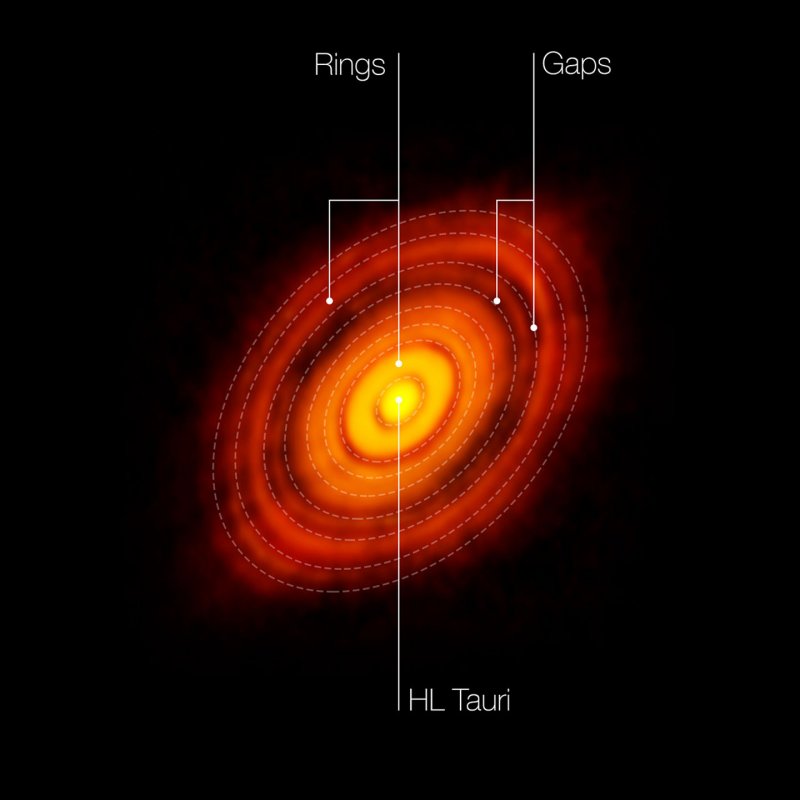
Also in space news, the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) captures our best look yet at potential planetary formation around a newborn star, 450 light years away. “The disk surrounding HL Tauri is much bigger than Neptune’s orbit, so any planet in the gaps would at least begin at a larger orbit than the major planets in the Solar System. Additionally, other gaps could be ‘resonances’: orbits where the combined gravity of the star and protoplanets drive matter out, concentrating it in the rings.”
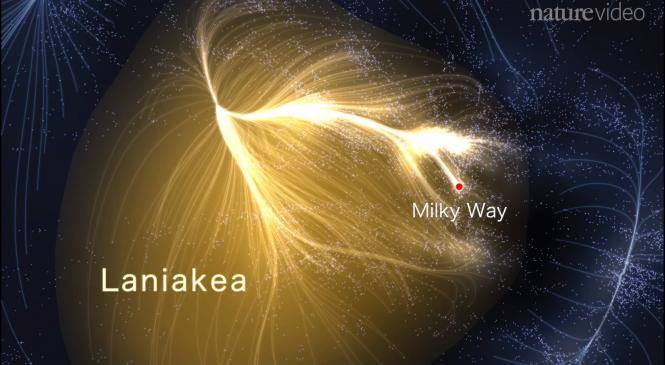
Using an algorithm based on the velocity of redshifting galaxies, a team of University of Hawaii astronomers identify our galaxy’s place in the newly-identified Laniakea supercluster. (Laniakea being Hawaiian for “Immeasurable Heaven.”) Adds Slate‘s Phil Plait: “Laniakea is about 500 million light years across, a staggering size, and contains the mass of 100 quadrillion Suns — 100 million billion times the mass of our star.”

By way of Follow Me Here, Gizmodo looks at five massive telescopes that will change the game, including the James Webb Space Telescope, a.k.a. Hubble 2.0. “Since blowing past its initial budget and launch data, NASA promises the ambitious project is on-track for 2018. And it better, because astronomers are eagerly awaiting its data.”
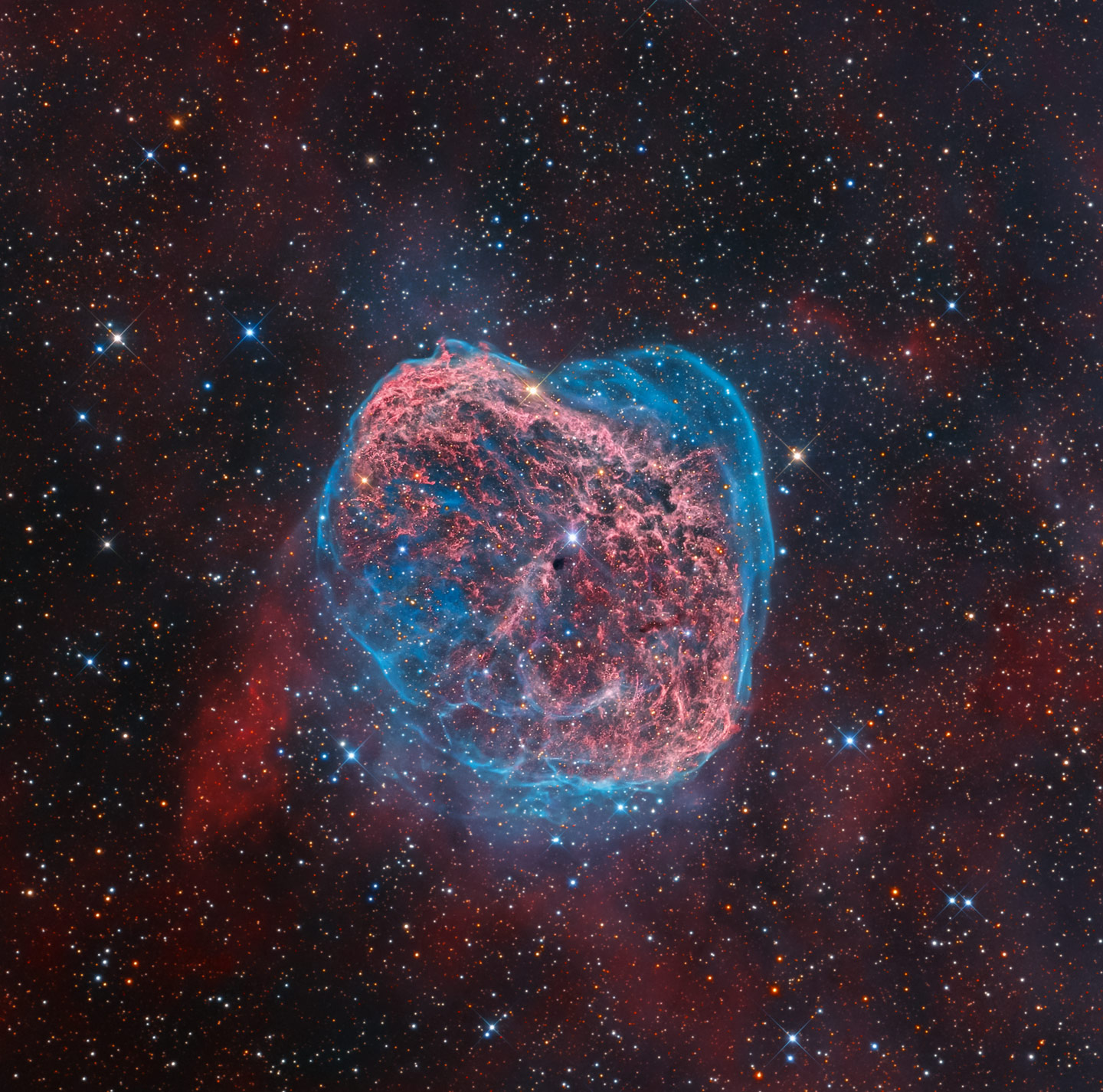

From attack ships on fire off the shoulder of Orion to c-beams glittering in the dark near the Tannhauser Gate, Slate’s Phil Plait shows off the winners of this year’s Astronomy Photographs of the Year. All 2500 submissions can be viewed here.

By incorporating quasars into the field of study, physicists determine the expansion rate of the universe to within 2.2 accuracy. That rate: 68 kilometers per second (which, for the Douglas Adams aficionados out there, translates into 42 miles per second.) “The uncertainty is plus or minus only a kilometer and a half per second.”

Once dismissed as a crank 30 years ago — this apparently happens to theorists of time often — an MIT professor finds his quantum theory of time gaining adherents. “Energy disperses and objects equilibrate…because of the way elementary particles become intertwined when they interact — a strange effect called ‘quantum entanglement.’…’What’s really going on is things are becoming more correlated with each other,’ Lloyd recalls realizing. ‘The arrow of time is an arrow of increasing correlations.'”
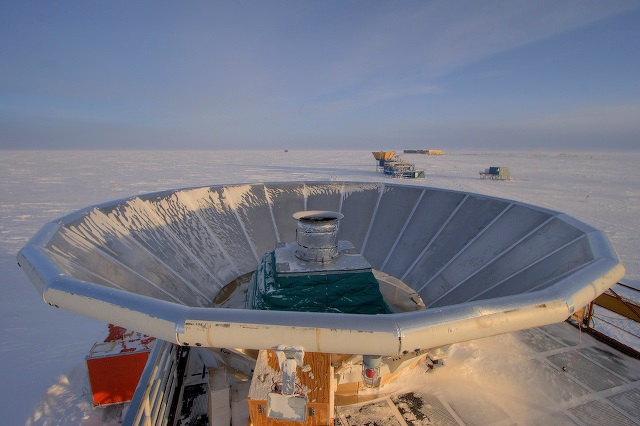

Until now? With help from the South Pole’s BICEP2 observatory, astrophysicists announce they have detected the first possible direct evidence of cosmic inflation after the Big Bang, in the form of “distortions in the cosmic microwave background light…Those distortions take the form of twisting of the light’s polarization created by gravitational disturbances from inflation.” “‘This has been like looking for a needle in a haystack, but instead we found a crowbar,’ said co-leader Clem Pryke.”
Update: 5 Sigma, R of 0.2. WHAT? Also another good explanation here: “Punchline: other than finding life on other planets or directly detecting dark matter, I can’t think of any other plausible near-term astrophysical discovery more important than this one for improving our understanding of the universe.”
Update 2: “The problem: the signal predicted by inflation is something called polarization, a sort of twisting of electromagnetic radiation. And while it can come from inflation-triggered gravity waves, microwaves from the early universe are altered en route to earthly telescopes, and if you don’t allow for the alteration, you can mistake local dust for a signal from billions of years ago.” Wait a tic: Princeton scientists cast doubt on the discovery.
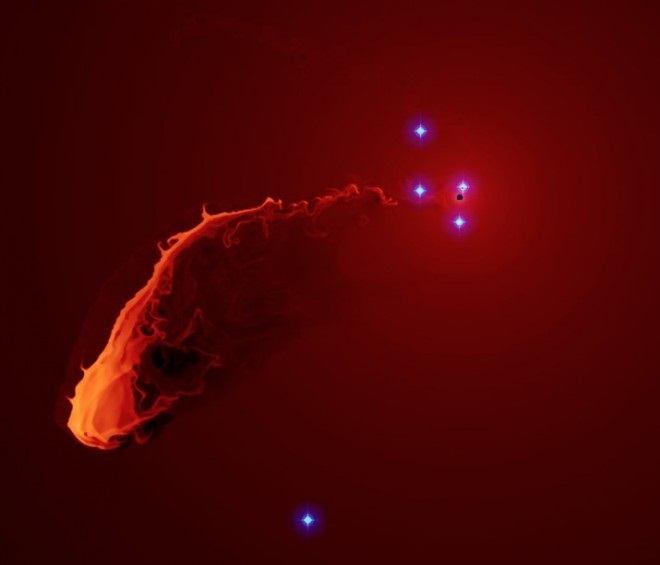
With an array of telescopes, astronomers are watching a gas cloud waft dangerously close to the supermassive black hole at the center of our galaxy “this month” (Of course, it already happened ages ago, and we’re just now being apprised of it.)
“The gas cloud…could either continue on its current orbit and slingshot around the black hole or it could run into surrounding gas and dust, which will make it lose speed and start sliding down toward the black hole. The first scenario could give scientists insight into the evolution of galaxies and better understand the history of our Milky Way’s own black hole. In the second case, they might get to watch the black hole consume a sizable dinner.” Say hi to Maximillian for me.
By way of Dangerous Meta and H-Twins, a handy and interactive chart of the scale of the universe. “The real genius of the interface is the ability to scroll back to a familiar object like a car — the time spent scrolling helps to convey a sense of size and distance.”