Using the relatively new technique of gravitational microlensing, astronomers discover their “most Earth-like planet yet”, orbiting a star in Sagittarius 20,000 light-years away. While this planet — currently named OGLE-2005-BLG-390Lb — is likely too cold for habitation, “‘we may predict with reasonable probability that microlensing will discover planets with masses like that of Earth at a similar distance from their stars and with comparable surface temperature,’ said study co-author Bohdan Paczynski from Princeton University.“
Tag: The Universe
Inconstant Cosmos.
“‘As you go back in time, the universe is pushing [outward] less and less,’ he said. ‘At some point, the pressure of dark energy is zero and is exerting no force on the universe. There is no explanation for it.'” New cosmological research announced yesterday further muddles our understanding of the expansion of the early universe and (once again) casts doubt on Einstein’s recently resurrected cosmological constant. “Schaefer based his findings on analysis of ultra-bright cosmic explosions called gamma-ray bursts, detected as far as 12.8 billion light-years away. He found that the most distant explosions appeared brighter than they should have been if the universe were accelerating at a constant rate.“
Under the Milky Way.
Via a friend in the program, the VR Milky Way Panorama. Definitely worth a spin.
In Search of M.
“String theory, the Italian physicist Dr. Daniele Amati once said, was a piece of 21st-century physics that had fallen by accident into the 20th century. And, so the joke went, would require 22nd-century mathematics to solve.” The New York Times surveys string theory at 20…fascinating stuff, but I still don’t get it.
Not Exactly Soundgarden.
“The more black holes eat, the more they spill, and it is widely thought that their feeding frenzies power the violence seen in the nuclei of many galaxies, including the powerful quasars that are so bright they outshine their parent galaxies.” The NY Times delves into the strange sounds emanating from black holes. “The frequency of these waves was equivalent to a B flat, 57 octaves below middle C, the astronomers calculated.“
Short-sighted NASA.
An outside panel of experts entreat NASA to save the Hubble, “arguably the most important telescope in history.” Given it’s been both a rare PR victory for the administration and an amazing source of scientific data, one would think the Hubble would remain a top priority, even despite all the new talk of Mars.
I See You.
Beware M64: There is an evil there that does not sleep…and the Great Eye is ever watchful.
More fun than Sea Monkeys!
If you thought Manhattan for $24 was a great deal, check this out…Entire galaxies for $19.99 each. Sure, the location’s terrible, but think of the space… (Via Footprints.)
Worth a Thousand Answers.
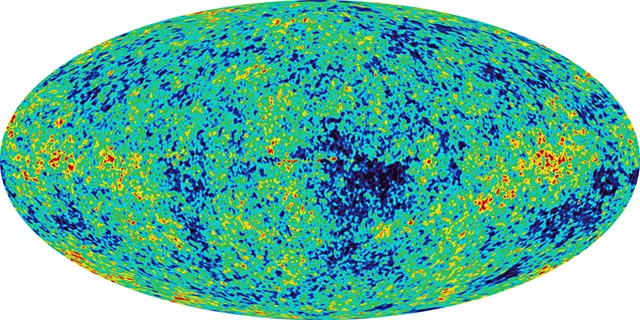
Big news and bold statements are issuing forth from Greenbelt, MD. “We’ve now laid the cornerstone of a unified cosmic theory…We have not answered all the questions. But we’ve certainly turned a corner.” Thanks to NASA and the Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP), scientists now have visual evidence of the universe’s origins with which to test out all the prevailing cosmological theories. Great news! Not only is any new empirical data in this field a boon to science, but, if ridiculous amounts of new information are gleaned from just this one little probe…well, it won’t help NASA in the manned space department, but the agency could still use a few unmitigated victories these days. On another note, looking at this map brings back some old memories. For my high school science thesis (required at SCGSSM), I used similar COBE DMR data to figure out that early galaxies displayed a fractal distribution. (Hey, it was the early ’90’s – fractals were the rage.) I wonder if this new data bears out that old rinky-dink thesis.
Schroedinger’s Universe.
Discover interviews physicist John Wheeler about the quantum nature of reality. “Wheeler conjectures we are part of a universe that is a work in progress; we are tiny patches of the universe looking at itself – and building itself. It’s not only the future that is still undetermined but the past as well. And by peering back into time, even all the way back to the Big Bang, our present observations select one out of many possible quantum histories for the universe.” (Via Anil Dash.)
